王义松
![]()
开通时间:..
最后更新时间:..
扫描访问手机版
点击次数:
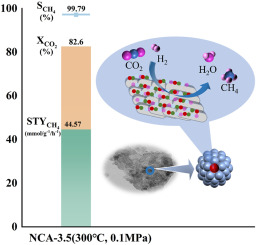
摘要:The methanation of carbon dioxide is a crucial pathway for carbon emission reduction and clean energy (CH4) production. The preparation of high-performance catalysts is a critical step in realizing this process. In this study, NiCu-Al2O3 bimetallic catalysts with different Ni/Al ratios (NCA-x, where x = 1.5, 3.5, and 5, as well as NA and CA) are prepared via the urea hydrolysis method. The NiCuAl trimetallic hydrotalcite precursor shows high crystallinity and uniform particle size distribution, providing a robust basis for NCA catalyst synthesis. Cu doping effectively suppresses Ni agglomeration, leading to a larger specific surface area, while increasing the Ni/Al ratio further improves crystallinity. At 300 °C and 0.1 MPa, all catalysts exhibit high methane selectivity, with CO2 conversion consistently above 60%. Notably, NCA-3.5 achieves 82.6% CO2 conversion, excellent surface area, strong reducibility, high surface Ni0 (6%), and the highest methane space–time yield (44.57 mmol·g-1·h-1). In a 72-hour test, CO2 conversion remains stable, with no obvious deactivation. At 280 °C, NCA-3.5 reaches 81.9% conversion, confirming superior low-temperature activity. XRD and TG analyses show no structural damage or significant carbon deposition, indicating excellent stability.
是否译文:否
上一条:Jia H, Du T*, Li Y, Wang Y*. Effect of a Grinding Method in the Preparation of CuO-ZnO-Al2O3@ HZSM-5 Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation[J]. Catalysts, 2025, 15(11): 1068.
下一条:Zhou X, Jia H, Chen W, & Wang, Y.* (2025). Novel Ag-modified g-C3N4 nanotubes with large specific surface area for efficient photocatalytic reduction of CO2[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2025, 462: 116211.